Are you an artist or someone who frequently works with turpenoid? If so, you know the incredible solvents that turpenoid can be, helping you achieve those mesmerizing brushstrokes or effectively clean your art tools.
However, have you ever wondered how to dispose of turpenoid responsibly? Improper disposal of this powerful substance can have detrimental effects on the environment and even pose safety risks. That’s where we come in.
In this guide, we will dive into the world of turpenoid disposal, equipping you with the knowledge and tools to tackle this critical issue head-on.
Get ready to embrace responsible practices and protect our planet. Let’s dive in!
What is Turpenoid?
Turpenoid is a solvent commonly used in various art mediums and cleaning products.

It is derived from the distillation of turpentine oil, making it a powerful and effective solution for dissolving paint, thinning oil-based materials, and cleaning brushes.
The composition of turpenoid typically includes hydrocarbons and organic compounds, providing it with its distinctive properties.
Artists often rely on turpenoid as a versatile solvent for oil painting, as it aids in diluting paints, creating washes, and achieving desired effects.
In addition, it serves as a valuable tool for brush cleaning and removing paint from palettes and other surfaces.
Turpenoid is also found in cleaning products, where its powerful solvent properties help in removing grease, stains, and other tough substances.
Why is Proper Disposal Important?
Improper turpenoid disposal can severely impact the environment and human health.
Environmental Impact: Turpenoid contamination degrades soil, harms plants, and disrupts water ecosystems. It also contributes to air pollution, posing respiratory health risks.
Legal and Safety Considerations: Proper disposal is legally required in many areas, with regulations mandating safe methods for hazardous substances. Non-compliance can lead to penalties. Safe disposal also prevents accidents, spills, and fires, protecting those handling turpenoid.
How to Dispose of Turpenoid: Methods
There are several methods available for disposing of turpenoid, each with its own advantages and considerations. Let’s explore three commonly used disposal methods:
Method 1: Reusing Turpenoid
Before considering disposal, evaluate the condition of your turpenoid for potential reuse. If the turpenoid appears clear and free of debris or excessive paint particles, it may be suitable for reuse.
However, it’s essential to remember that reused turpenoid may lose its effectiveness over time.
To ensure proper storage and usability of reusable turpenoid:
- Transfer the turpenoid to a clean, airtight container.
- Label the container with the date and contents.
- Store the container in a cool, well-ventilated area, away from heat and flames.
Method 2: Recycling Turpenoid
Recycling turpenoid is an eco-friendly option that helps reduce environmental impact. Check with local recycling centers or hazardous waste facilities to determine if they accept turpenoid for recycling.
Follow these steps to prepare turpenoid for recycling:
- Ensure the turpenoid container is tightly sealed to prevent leaks.
- Check with the recycling center for any specific packaging requirements.
- Transport the turpenoid to the recycling facility in a secure, upright position.
Method 3: Contacting Hazardous Waste Disposal Facilities
Hazardous waste disposal facilities are equipped to handle and manage substances like turpenoid safely. Locate a certified facility in your area by contacting local authorities or referring to directories.
When contacting hazardous waste disposal facilities:
- Inquire about their acceptance of turpenoid and any specific requirements.
- Follow their instructions for packaging and transporting turpenoid safely.
- Ensure proper labeling on the container to indicate its hazardous nature.
Method 4: Evaporating Turpenoid Safely
Evaporating turpenoid involves allowing it to evaporate naturally. However, it’s crucial to proceed with caution due to potential health and safety risks.
Follow these precautions and safety measures for safe evaporation:
- Choose a well-ventilated area with proper airflow, such as outdoors or a well-ventilated room.
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including gloves and a respirator if necessary.
- Avoid open flames or sparks, as turpenoid vapors are flammable.
- Monitor the evaporation process to ensure it occurs gradually and without incidents.
Method 5: Solidifying Turpenoid for Disposal
Solidifying turpenoid before disposal can help contain and minimize the risk of leaks or spills.
Follow these steps to solidify turpenoid:
- Pour the turpenoid into absorbent material like cat litter, sawdust, or a commercial solidifier.
- Mix the turpenoid and absorbent material until it forms a thick, paste-like consistency.
- Allow the mixture to solidify completely.
- Dispose of the solidified turpenoid according to local regulations and guidelines.
Alternative Solutions for Turpenoid Disposal
In addition to the aforementioned methods, there are alternative solutions for disposing of turpenoid responsibly.
A. Natural and Non-Toxic Substitutes for Turpenoid
There are two types of natural and non-toxic substitutes for turpenoid-
Vegetable Oil
Consider using vegetable oil as a natural substitute for turpenoid. It can effectively thin oil paints and clean brushes without the harmful effects of traditional solvents.
Here’s how to use vegetable oil as a substitute:
- Thinning Oil Paints: Instead of using turpenoid to thin oil paints, mix a small amount of vegetable oil directly into the paint on your palette.
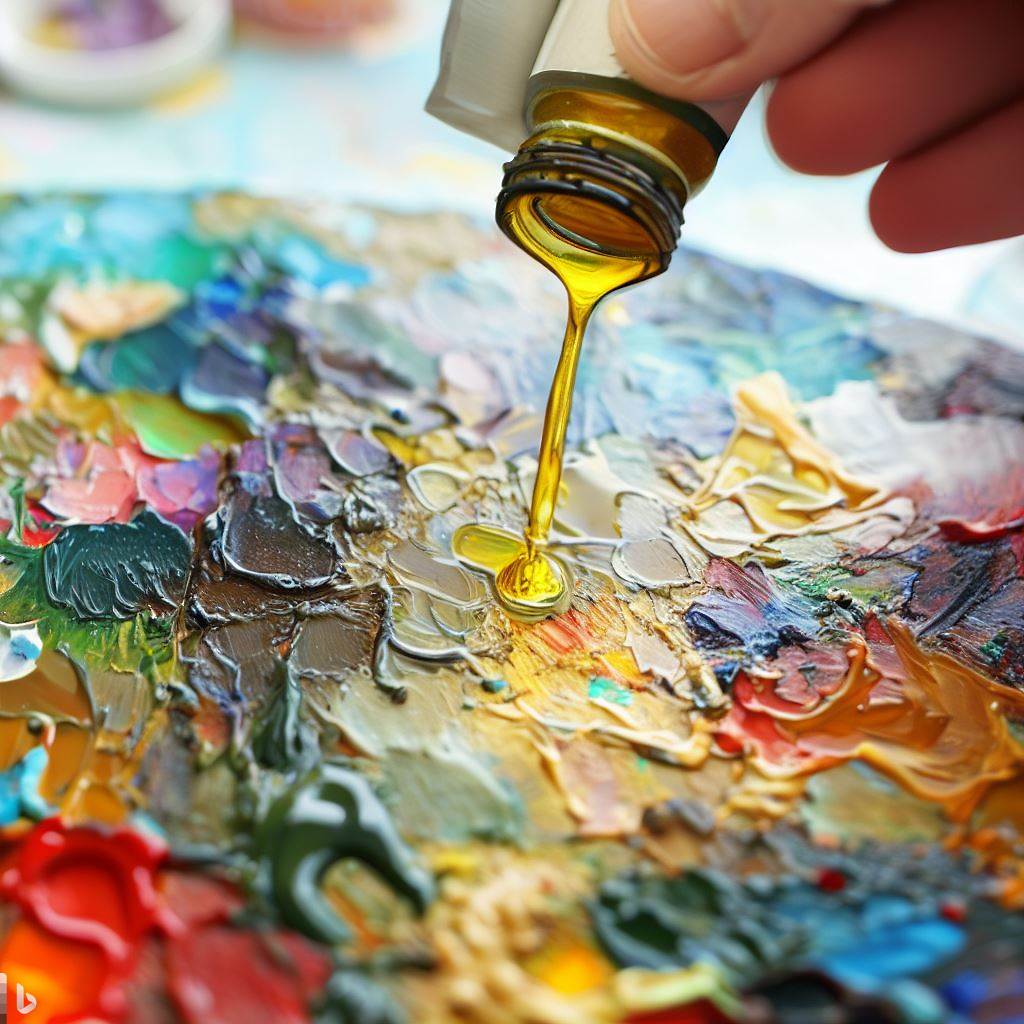

Adding vegetable oil to the paint
Start with a small quantity and gradually add more if needed. This method allows you to achieve the desired consistency while keeping the paint workable.
- Cleaning Brushes: After painting, wipe off excess paint from your brushes using a cloth or paper towel. Then, dip the brushes into a container with vegetable oil and gently swirl them around to loosen the remaining paint.
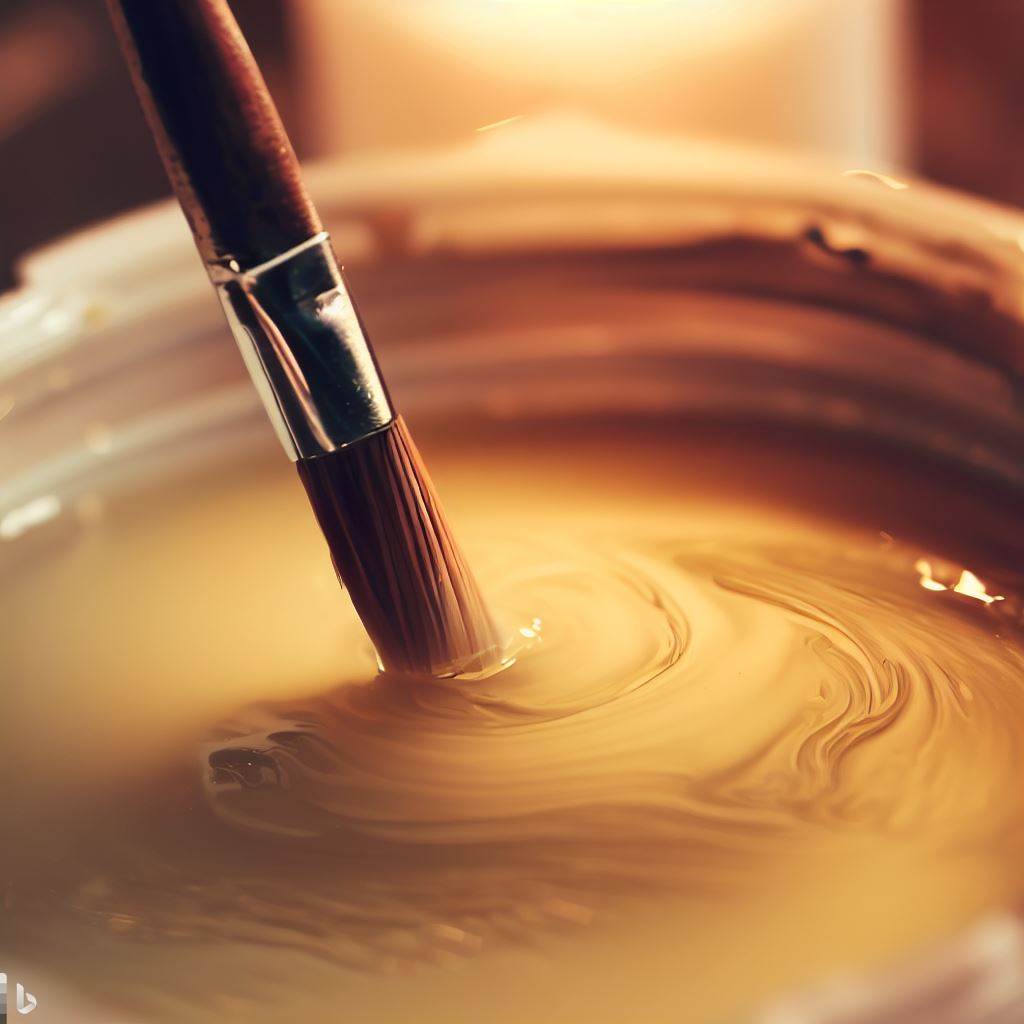

Dipping the paintbrush into the vegetable oil
Rinse the brushes with mild soap and warm water, followed by a thorough rinse to remove any residual oil. Finally, reshape the bristles and allow the brushes to air dry.
Citrus-Based Cleaners
Citrus-based cleaners, derived from orange or lemon peels, offer a non-toxic alternative for paint thinning and brush cleaning. These cleaners are biodegradable and emit a pleasant scent.
Here’s how to incorporate citrus-based cleaners into your art practice:
- Thinning Paints: Instead of using turpenoid, mix a small amount of citrus-based cleaner with your oil paints on the palette. Gradually add the cleaner to achieve the desired consistency.
Keep in mind that these cleaners may evaporate faster than turpenoid, so work efficiently.
- Brush Cleaning: Similar to vegetable oil, citrus-based cleaners can be used to clean brushes effectively. After wiping off excess paint, dip your brushes into a container with the citrus-based cleaner and gently agitate them.
Rinse the brushes with mild soap and warm water, ensuring all residual cleaner is removed. Reshape the bristles and allow the brushes to air dry.
B. Safer Solvent Disposal Options
There are two types of solvent for safer solvent disposal options-
Water-Based Solvents
Water-based solvents, such as acrylic mediums or water-mixable oils, are an excellent alternative to turpenoid. They can be easily cleaned with soap and water, eliminating the need for hazardous waste disposal.
Bio-Based Solvents
Bio-based solvents are derived from renewable resources such as plants, and they offer a greener option for paint thinning and brush cleaning.
Some examples include soy-based solvents and ethanol made from agricultural waste.
- Soy-Based Solvents: Soy-based solvents are eco-friendly alternatives that effectively dissolve oil-based paints and varnishes. They have low toxicity and emit fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) compared to traditional solvents.
- Ethanol from Agricultural Waste: Ethanol produced from agricultural waste, such as corn husks or sugarcane bagasse, is another bio-based solvent option. It can be used for paint thinning and cleaning brushes, providing a sustainable alternative.
Disposal of Turpenoid Soaked Materials
Turpenoid-soaked materials such as rags, brushes, or other tools require special attention during disposal. Due to their contamination, they can pose additional risks.
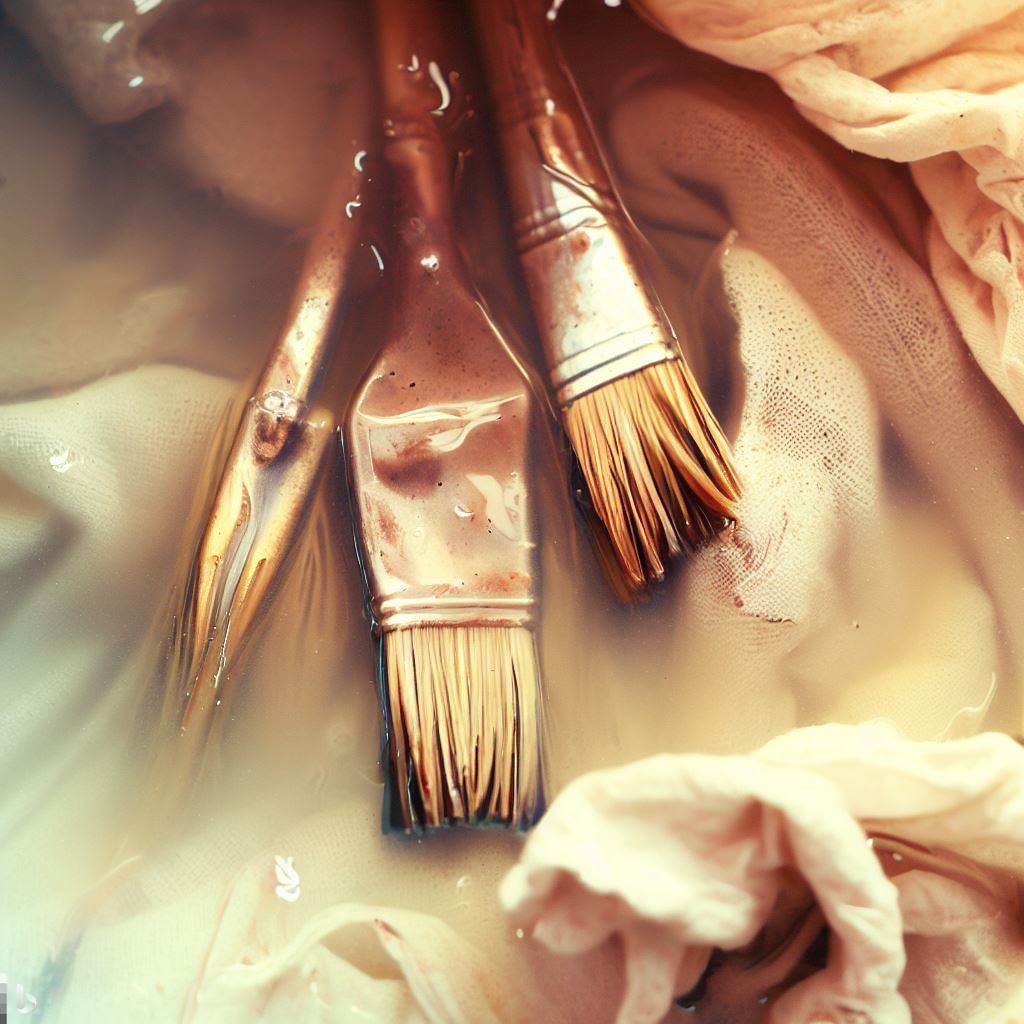

Turpenoid-soaked rags and brushes
Follow these guidelines for their proper disposal:
- Place turpenoid-soaked materials in a sealed, leak-proof container.
- Label the container as hazardous waste and indicate its contents.
- Contact local authorities or hazardous waste facilities for specific instructions on their disposal.
Avoiding Accidental Ignition or Release During Disposal
To prevent accidents, fires, or accidental release during the disposal process, it’s crucial to take necessary precautions:
- Keep turpenoid and turpenoid-soaked materials away from heat sources, open flames, or sparks.
- Use appropriate storage containers that are designed for hazardous materials.
- Store and transport containers in an upright position to prevent leaks or spills.
FAQs
- What should I do if there are no hazardous waste facilities nearby?
If hazardous waste facilities are not accessible, contact local waste management authorities for alternative disposal options. They may provide guidance on specific collection events or alternative disposal methods that comply with regulations.
- Can I dispose of turpenoid in regular household trash?
Turpenoid should not be disposed of in regular household trash. It is considered hazardous waste and requires special handling. Contact hazardous waste facilities or waste management authorities for proper disposal options.
- Can I mix turpenoid with other substances for disposal?
Mixing turpenoid with other substances for disposal can be dangerous and may result in chemical reactions or increased hazards. Follow the recommended disposal methods and avoid mixing turpenoid with other materials unless specifically instructed to do so by professionals.
- Can I burn turpenoid for disposal?
Burning turpenoid for disposal is not recommended. It can release toxic fumes, contribute to air pollution, and pose fire hazards. Always opt for safer disposal methods like recycling, reusing, or contacting hazardous waste disposal facilities.
Wrapping Up
As we reach the ending of our journey on how to dispose of turpenoid, let us reflect on the importance of responsible waste management and the impact it has on our environment.
By now, you have gained valuable insights into the definition and composition of turpenoid, understood the significance of proper disposal methods, and explored various techniques to dispose of turpenoid safely and ethically.
By adopting best practices for turpenoid disposal, researching local regulations and guidelines, and educating others, you become an advocate for environmental preservation.
If disposing of Turpenoid feels cumbersome, you might want to explore the list of non-toxic solvents for oil painting to find safer and more eco-friendly options.